Business location
General objective: Low cost - high revenue = high profit
Special factors:
Special industries need
→ water source for waste disposal or cooling
→ the right climate for the production of a good
→ a location near the source of raw materials (weight-losing industries, e.g. coal, copper, forest industries, sugar mills
→ a location near the market for a good (weight- or bulk-gaining industries, which produce final products that are heavier or bulkier than the raw materials, usually by addition of some ubiquitous raw material such as water, e.g. beer industry)
Footlose industries
→ gain no particular advantage from any one location, usually because transport costs are the same for each site or very low
Business location factors may be split up into 4 categories:
- Quantitative factors: cost factors
- Qualitative factors: factors that cannot be quantified but may have a significant impact on the location decision
- Market-side factors: look at output/possible profits
- International factors: additional factors for international location decisions
Such location factors may be:
Quantitative factors
Fixed costs:
- Site costs
- Availability of incentives: grants/subsidies/allowances
- Cost of loans
- Cost of utilities: gas, water, electricity
- Tax rates
- Cost of fixed salary staff
- Cost/availability of technology
Variable costs
- Cost of raw materials/ commodities
- Cost of sourcing supplies/availability of suppliers
- Transportation costs
- Cost of skilled/unskilled labour
- Waste management/infrastructure
Qualitative factors
- Quality of infrastructure: roads, rail links, schools, bandwidth, etc.
- Quality of labour supplies
- Health and safety
- Opportunities for expansion
- Ease with which planning consent can be achieved
- Possible external economies of scale (advantages resulting from other firms locating in the region)
- Nearness to a supply of skilled/unskilled labour
- Environmental restrictions
- Quality of suppliers
- Nearness to research centres/lawyers etc.
- Image of location
Market-side factors
- Competition
- Nearness to market
- PC ownership
- Sales infrastructure: processing payments and sales
- Growth of market
- Purchasing power
- Market volume
- International competitors
- Market shares
- Distribution channels
- Customer preferences
- Strategies of competitors
Additional factors for international location decisions
- Legislation: esp. concerning employment (working hours/flexibility), tax laws, trade laws
- Ease of access to international markets
- Possible language/cultural issues (religion, women, working culture, trading customs, values)
- Political stability
- Economic stability
- Productivity
- Amount of bureaucracy
-
Social security - Existence of trade barriers and non-tariff barriers
 / trade blocs
/ trade blocs
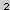
- Interest rates (capital costs)
- Exchange rates
- Growth of GDP
- Inflation
- Foreign and domestic investment
- Ecological situation
- Restriction for foreign staff (work permits etc.)
- Attainable product quality
- Delivery times
- Customer needs
Location factors may also be separated into push factors (e.g. rising competition in an area, rising costs, poor communications systems, falling demand) and pull factors (e.g. government incentives, low labour costs, good communication systems, developing markets)
 Non-tariff barriers may be:
Non-tariff barriers may be:
|
|||||
 e.g. Japanese companies building plants in the EU to help overcome the Common External Tarif
e.g. Japanese companies building plants in the EU to help overcome the Common External Tarif
|
Dokument herunterladen [.doc][40 KB]